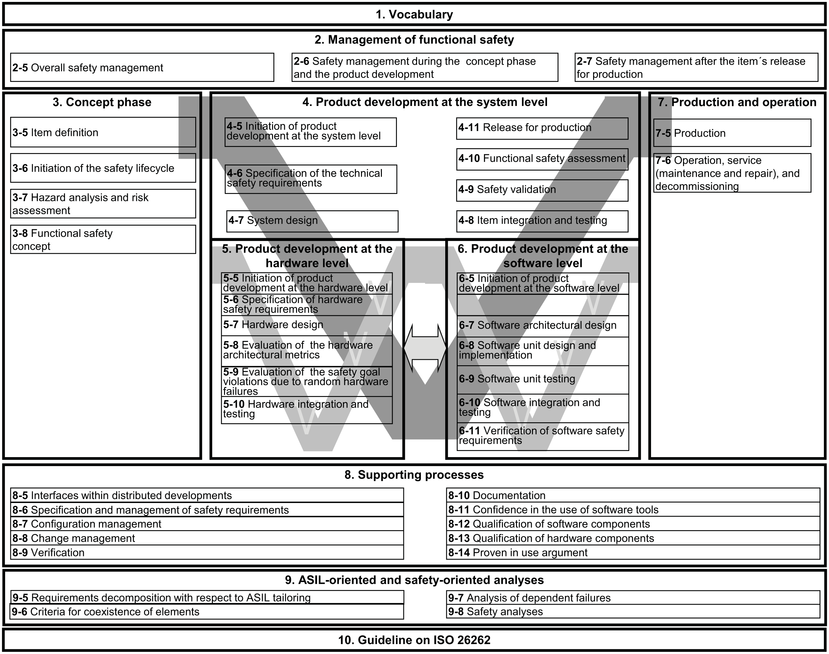
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive engineering, functional safety has become a cornerstone of vehicle development. At the heart of this process lies ISO 26262, the international standard for functional safety in road vehicles. This article delves into one of the most critical stages of the ISO 26262 lifecycle: the Concept Phase. What is the Concept Phase? The Concept Phase is the initial stage of the ISO 26262 safety lifecycle, setting the foundation for all subsequent safety activities[1][6]. It’s during this phase that automotive engineers and safety experts lay the groundwork for ensuring the safety of electrical and electronic systems in vehicles. Key Objectives of the Concept Phase The primary goals of the Concept Phase include: Steps in the Concept Phase 1. Item Definition The first step is clearly defining the “item” – the system or component under consideration[1]. This involves: Outlining the system’s functionality Identifying its boundaries and interfaces Describing its interactions with other systems 2. Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) HARA is a crucial step where potential hazards are identified and risks are evaluated[1]. This process involves: Identifying potential hazardous events Assessing the severity, exposure, and controllability of each hazard Determining the Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) 3. Safety Goals Formulation Based on the HARA results, safety goals are established. These high-level safety requirements aim to mitigate identified risks[6]. 4. Functional Safety Concept Development This step involves: Deriving functional safety requirements from safety goals Allocating these requirements to architectural elements Defining safety mechanisms 5. Validation Planning The final step in the Concept Phase is planning for the validation of safety requirements throughout the development process[2]. Importance of the Concept Phase The Concept Phase is critical because: Best Practices for the Concept Phase To maximize the effectiveness of the Concept Phase: Involve a diverse team of experts Use structured methods for hazard analysis Document all decisions and rationales thoroughly Consider both normal operation and reasonably foreseeable misuse Challenges in the Concept Phase Some common challenges include: Accurately defining system boundaries Ensuring completeness in hazard identification Balancing safety requirements with other product attributes Conclusion The Concept Phase of ISO 26262 is a crucial step in ensuring the functional safety of automotive systems. By thoroughly identifying hazards, assessing risks, and establishing safety goals early in the development process, automotive manufacturers can create safer vehicles while optimizing development costs and timelines. As the automotive industry continues to evolve with advanced technologies like autonomous driving and electric powertrains, the importance of a robust Concept Phase in functional safety will only grow. Engineers and safety experts must stay abreast of best practices and emerging methodologies to ensure the continued safety and reliability of road vehicles.
📊 Did you know? Businesses with a strong digital presence grow 4 times faster than those without one! [Source: Google’s Economic Impact Report] At Xenban, we harness the power of digital marketing to help your business achieve this kind of growth. Here’s a look at our tried-and-tested 5-step process: 1️⃣ Research & Planning: We conduct thorough market research, setting clear goals and KPIs to ensure your strategy is aligned with your business objectives. 2️⃣ Content Creation & Strategy: Our tailored, SEO-optimized content captures attention and converts leads through engaging copy and visuals. 3️⃣ Campaign Implementation: From PPC ads to social media and email marketing, we implement strategies designed to deliver measurable results. 4️⃣ Monitoring & Analytics: Using advanced analytics, we track performance, run A/B tests, and gather feedback to refine your campaigns continuously. 5️⃣ Optimization & Scaling: We analyze data to scale successful campaigns, driving sustained growth and a better ROI. Ready to take your digital marketing to the next level? Let Xenban lead the way! 🌐 📩 Contact us today and let’s get started.
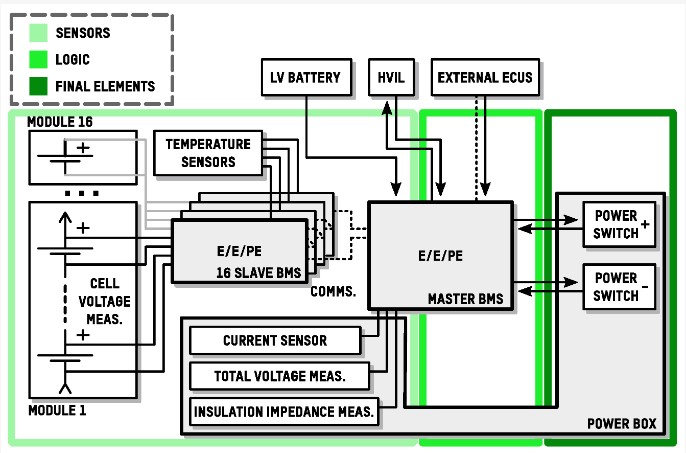
🔋 Ensuring Functional Safety in Battery Management Systems (BMS): Key Requirements 🔋 With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems, the functional safety of Battery Management Systems (BMS) is paramount. Here’s a detailed overview of essential safety requirements to enhance BMS reliability and performance: 🔴 Battery State Monitoring✅Real-Time Monitoring: Implement sensors to monitor voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SOC).✅Redundant Systems: Ensure redundant monitoring to detect sensor failures.✅Diagnostics: Provide real-time diagnostics for early fault detection. 🟢 Cell Balancing and Management✅Balancing Techniques: Implement active/passive cell balancing to maintain uniformity.✅Voltage Monitoring: Continuously monitor cell voltages to detect imbalances.✅Thermal Management: Ensure effective thermal management to prevent overheating. 🟡 Overcharge and Overdischarge Protection✅Voltage/Current Limits: Set precise limits to prevent overcharge and overdischarge.✅Cutoff Mechanisms: Implement mechanisms to disconnect the battery if limits are exceeded.✅Alarms and Notifications: Provide alerts for abnormal conditions. 🔵 Short Circuit and Overcurrent Protection✅Fast-Acting Fuses: Use fuses and circuit breakers to protect against short circuits.✅Current Sensing: Integrate current sensing and limiting features.✅Fault Detection: Provide mechanisms for real-time fault detection and isolation. 🔴 Thermal Management✅Cooling/Heating Systems: Implement systems to manage battery temperature.✅Temperature Monitoring: Monitor temperature across cells and modules.✅Thermal Runaway Detection: Provide detection and mitigation strategies. 🟢 Communication and Data Integrity✅Robust Protocols: Use reliable communication protocols (e.g., CAN, LIN).✅Error Detection: Implement error detection and correction mechanisms.✅Data Logging: Ensure traceability for diagnostic purposes. 🟡 Functional Safety Management✅Safety Culture: Foster a safety culture emphasizing functional safety at all levels.✅Compliance: Ensure adherence to standards (e.g., ISO 26262, IEC 61508).✅Safety Audits: Conduct regular audits and reviews. 🔵 Verification and Validation (V&V)✅System Testing: Perform extensive testing, including Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) and Software-in-the-Loop (SIL) simulations.✅Fault Injection Testing: Simulate faults to verify fault tolerance.✅End-to-End Validation: Validate safety mechanisms comprehensively. 🔴 Continuous Monitoring and Updates✅Safety Performance: Implement continuous monitoring of safety performance.✅Software Updates: Provide regular updates and patches.✅Periodic Assessments: Conduct regular safety assessments and improvements. At Xenban we help companies to define, deploy and implement functional safety requirements. Please visit www.xenban.com to know about products and services.
Introduction: XYZ Manufacturing is a leading company in the production of chemical products. The company operates a state-of-the-art chemical processing plant that relies heavily on an intricate Industrial Control System (ICS) to ensure the efficiency and safety of the manufacturing processes. Recently, the management recognized the need to enhance functional safety within the ICS to meet evolving industry standards and regulatory requirements. Background: The existing ICS, which had been in operation for several years, was designed to control various critical processes such as mixing, reaction, and temperature control. The safety measures in place included emergency shutdown systems and process alarms. However, with advancements in technology and updated safety standards, XYZ Manufacturing identified the necessity to reassess and improve the functional safety of their ICS. Challenges: Several challenges were identified in the current state of the ICS: Objectives: The primary objectives of the safety enhancement project were: Implementation: To achieve these objectives, XYZ Manufacturing collaborated with a functional safety expert and implemented the following steps: Results: The implementation of the safety enhancement project yielded significant results: Conclusion: By prioritizing functional safety and undertaking a comprehensive enhancement project, XYZ Manufacturing successfully modernized its ICS, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. The company’s commitment to safety not only protected its assets and operations but also contributed to the overall well-being of its employees and the surrounding community. This case study underscores the importance of regularly reassessing and updating functional safety measures in industrial settings. Notice: JavaScript is required for this content.
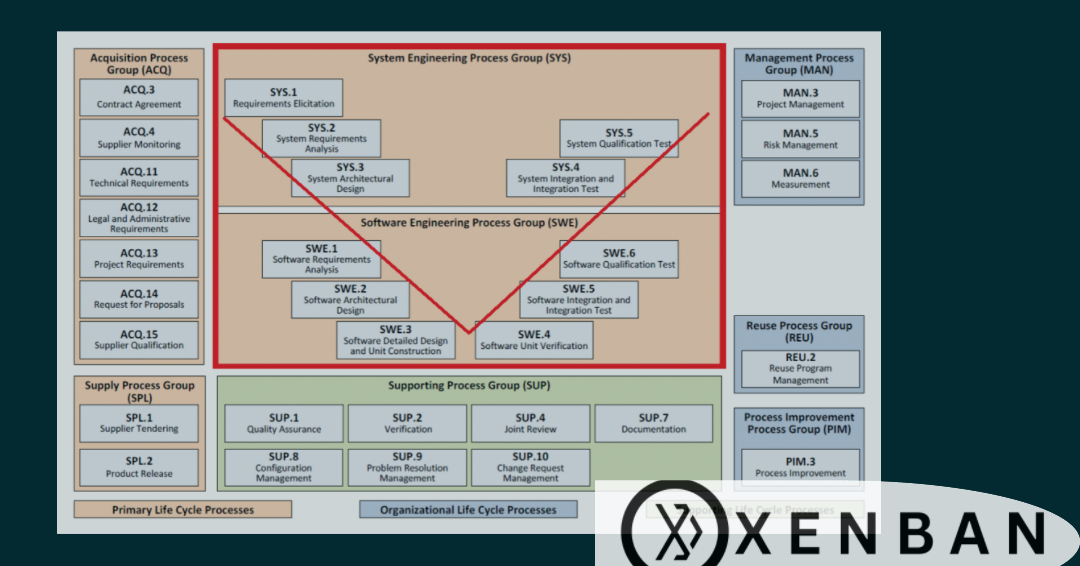
Implementing Automotive SPICE (Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination for the Automotive Industry) can pose several challenges, including: ✅Complexity: Automotive SPICE is comprehensive and involves complex processes. Adapting existing workflows to align with its requirements can be challenging, especially for organizations with well-established but different processes. ✅Resource Allocation: Implementing Automotive SPICE requires dedicated resources, both in terms of personnel and time. Assigning skilled personnel to understand, implement, and monitor these processes can be demanding. ✅Cultural Shift: Often, organizational culture and mindset need to change to embrace new processes and methodologies prescribed by Automotive SPICE. This cultural shift might face resistance or reluctance from some team members. ✅Training and Skill Enhancement: Teams may require training to understand the framework and its implications thoroughly. This involves investing in workshops, courses, and certifications, which can be time-consuming and costly. ✅Documentation Burden: Automotive SPICE requires extensive documentation to ensure compliance. Maintaining detailed documentation throughout the software development lifecycle can be labor-intensive. ✅Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating Automotive SPICE with existing systems, tools, and methodologies used in an organization may present compatibility challenges. ✅Vendor and Supplier Collaboration: For companies working with multiple vendors or suppliers, aligning their processes with Automotive SPICE requirements can be challenging and might require coordination and cooperation. Addressing these challenges often involves a phased approach, clear communication, and commitment from all levels of the organization to successfully implement Automotive SPICE. About Xenban; Xenban is an Engineering services company which helps companies to improve the Quality, safety and security of the products through Consulting, training and implementation. Our team can provide the best solution for the organizations to reach the business and product Goals. Contact our sales team at sales@xenban.com for free consulting and trainings. Visit www.xenban.com for more information on products and services.
Here are benefits of implementing ASPICE in the process to improve the capability. Ensuring compliance and safety: ASPICE compliance gives your company a solid foundation for safety engineering. Aside from staying in-line with regulatory authorities, compliance also opens business opportunities as car makers look to ASPICE compliance as a sign of quality software. Improving project management: ASPICE gives you control and visibility into the development progress and helps you manage increasingly complex projects. Risk mitigation: ASPICE requires organizations to establish risk management processes. Steps include identifying risks, analysing their impact, risk mitigation, and continuous monitoring Satisfying changing market demands: According to the World Economic Forum, “90% of future differentiating car features are software-based.” To keep up with these developments, ASPICE compliant automotive software related suppliers will play an increasingly large role in satisfying customer demands Above mentioned benefits are few of the major benefits. A product or software will be benefitted a lot if the ASPICE processes are implemented. At Xenban we provide consultation on implementing ASPICE, defining processes, performing Audits and Assessments to reach the goal of achieving ASPICE Capability and Maturity. Please contact out sales team sales@xenban.com for more information.
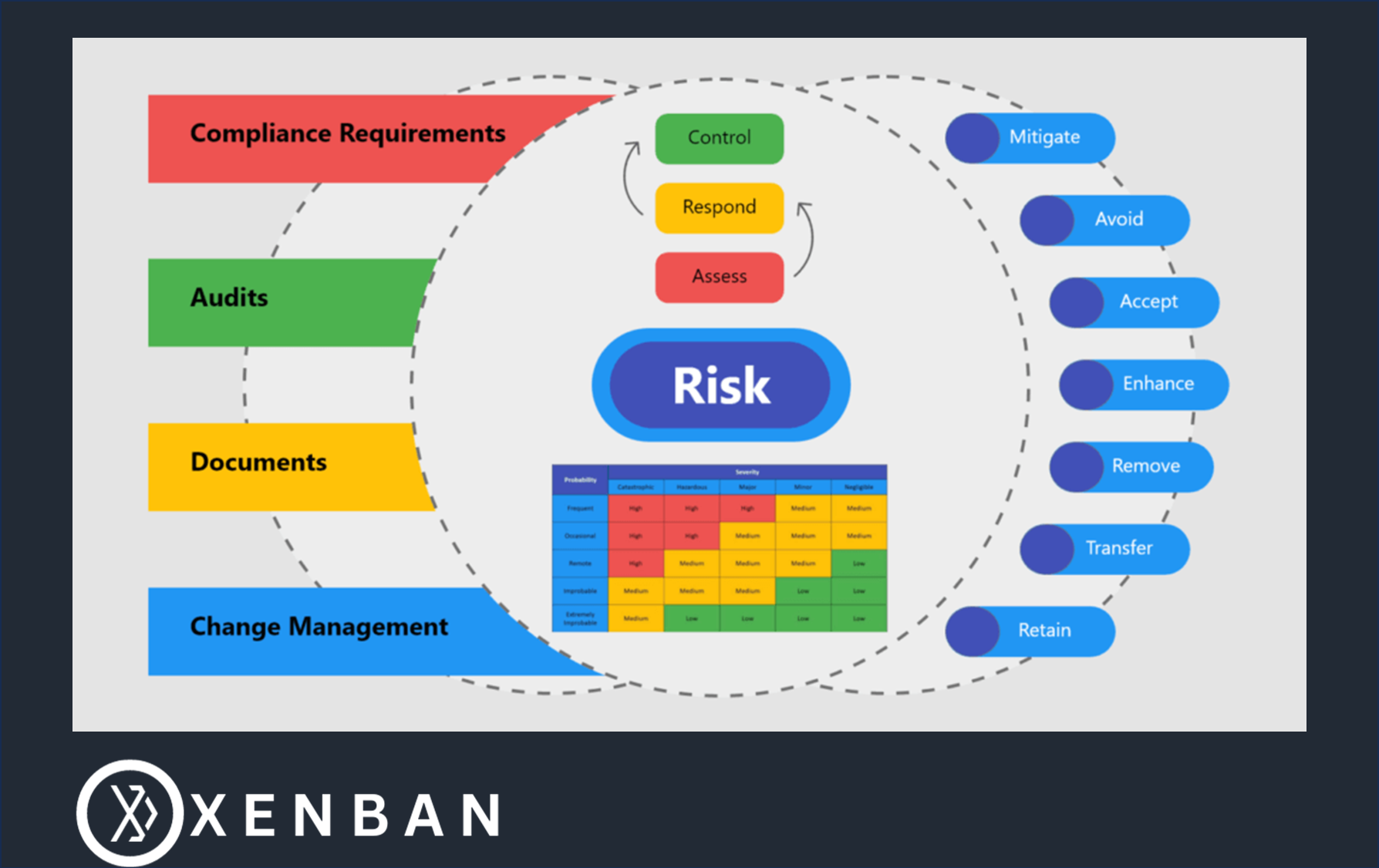
Risk Management elements: Roll out a business strategy that aims to identify, assess, and prepare for any dangers, hazards, and other potentials for disasters that may impact your organization’s operations and goals. Similarly, identify opportunities and assess them, and maximize benefits by putting plans to address positive risks. Introduce plans of actions, and make them accessible to all stakeholders. Ensure all risks and opportunities are under control while running the business successfully exceeding customers and stakeholders’ expectations. Setup and define risk responses of different types:o Mitigateo Avoido Accepto Enhance Define plan of actions for each risk response, defining what needs to be done immediately, and what needs to be done based on a risk trigger. Have the different actions assigned to the team to ensure parallel processing with full collaboration.Setup controls with drills and tests to ensure your risks and opportunities are controlled by a solid process in place. Reassess your risks to ensure they are mitigated to acceptable levels. Ensure all risks are in a controlled state and run. Iteratively identify new risks based on changing business climate and address them. At Xenban we digitalize the process in tools. The above described process can be defined in a ERP tool to manage the Risks and take necessary actions against them. Contact sales@xenban.com for more information about our services and products.
The main communication points from the CMMI Institute for V2.0 are: Improve Business Performance: Business goals are tied to operations in order to drive measurable improved performance.Leverage Current Best Practices: CMMI V2.0 is a trusted source of proven best practices.Build Agile Resiliency and Scale: The model contains direct guidance on how to strengthen Agile with Scrum.Benchmark Capability and Performance: The new performance-oriented appraisal method improves the reliability and consistency of benchmarking while reducing preparation time and lifecycle costs.Accelerate Adoption: Online platform and adoption guidance make the benefits of CMMI more rapidly achievable.Changed “Process Area” to “Practice Area”: This emphasizes that the model is not a collection of (rote) processes to be implemented, but a collection of practices to be used to run and manage projects.Organized practices within each Practice Area: Practices are organized by levels instead of Specific Goals. Levels provide a clear, methodical path for building capability and improving performance within each Practice Area.Replaced the Generic Practices with two new Practice Areas: Governance (GOV) & Implementation Infrastructure (II) to reduce the redundancy and complexity of the Generic Practices. They foster the persistence and habit of an organization’s processes and their business value rather than compliance to the model. At Xenban we provide services on CMMI consulting, Audit, Gap Analysis, Training and Citification Supports. Please contact our Sales team sales@xenban.com for more information.
SO 9001:2015 Quality Management System Requirements,We have broken down ISO 9001: 2015 to make it easier to understand and apply. ISO 9001: 2015 is the latest revision of ISO 9001. In this, there are 10 sections or clauses with supporting sub-sections (sub-clauses). Here is the summary of each clause. Clause 0 : IntroductionThis section introduces the purpose, principles and key concepts of the standard, including risk-based thinking and the process approach. Clause 1 : ScopeThis section defines the scope of the 9001:2015 standard. In summary, the scope includes specifying requirements for a QMS of any organization. Clause 2 : Normative ReferencesThe supporting standard referenced in ISO 9001:2015 and is indispensable for its application is ISO 9000:2015 which covers terminology and fundamentals. This and other supporting standards make up the 9000 series Clause 3 : Terms and Definitions Terminology used throughout this standard comes directly from ISO 9000:2015, Quality management systems – Fundamentals and vocabulary. Clause 4 : Context of the OrganizationDetermine external and internal issues, the needs and expectations of interested parties, quality management system scope and its processes. Clause 5 : LeadershipTop management to demonstrate leadership and commitment, establish and communicate a quality policy, and ensure responsibilities and authorities are assigned, communicated and understood Clause 6 : PlanningOrganizational Quality Management System Planning to address organizational risks, opportunities, changes and quality objectives. Clause 7 : SupportProvide resource needs, ensure employees are competent and aware, and include documented information to support your quality management system. Clause 8 : OperationPlan and control processes needed to meet the requirements for products and services (Design and development, external providers, production and service provision, release of products and services, nonconforming outputs). Clause 9 : Performance EvaluationMonitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate your quality management system. Clause 10 : ImprovementSelect opportunities for improvement, take action against nonconformists, implement corrective actions as necessary, and continually improve your quality management system. At Xenban, we provide services on defining QMS, Quality Consulting, ISO Trainings, Audits, Certification support. Please contact our sales team sales@xenban.com for more information,