Executive Summary
In the rapidly evolving automotive industry, software has become a critical component of vehicle functionality and innovation. As automotive manufacturers increasingly rely on suppliers for software development, effective supplier monitoring has become paramount. ASPICE ACQ.4, a key process in the Automotive SPICE framework, provides a structured approach to supplier monitoring, ensuring quality, timeliness, and compliance throughout the supply chain.
This whitepaper explores the intricacies of ASPICE ACQ.4 Supplier Monitoring, offering insights into best practices, challenges, and future trends. By implementing robust supplier monitoring processes, automotive companies can significantly reduce risks, improve product quality, and accelerate time-to-market. Our expertise in ASPICE consulting positions us uniquely to guide organizations through the complexities of supplier monitoring, ultimately driving success in automotive software development.
1. Introduction to ASPICE ACQ.4 Supplier Monitoring
1.1 Definition and Purpose
ASPICE ACQ.4 Supplier Monitoring is a process within the Automotive SPICE framework that focuses on overseeing and managing supplier activities throughout the software development lifecycle. Its primary purpose is to ensure that suppliers meet the agreed-upon requirements, adhere to quality standards, and deliver products or services on time and within budget.
1.2 Importance in Automotive Software Development
In the automotive industry, where software complexity is increasing exponentially, effective supplier monitoring is crucial for several reasons:
- Quality Assurance: Ensures that supplied software components meet the stringent quality standards required in automotive applications.
- Risk Mitigation: Helps identify and address potential issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of costly recalls or safety hazards.
- Compliance: Assists in maintaining compliance with industry regulations and standards, such as ISO 26262 for functional safety.
- Cost Control: Enables better management of development costs by preventing overruns and identifying inefficiencies.
1.3 Key Process Outcomes
The ASPICE ACQ.4 process aims to achieve several key outcomes:
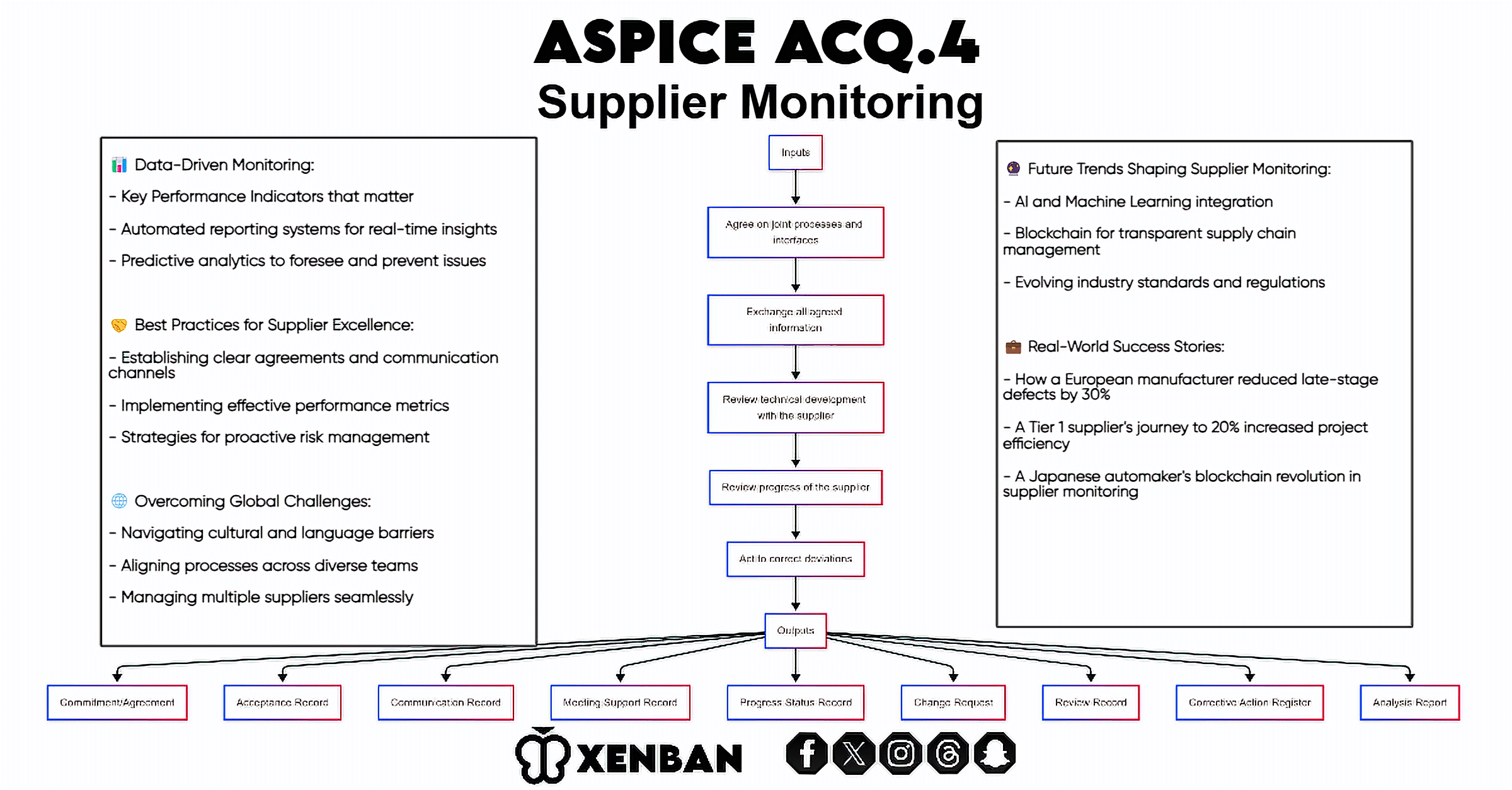
- Establishment of joint processes and interfaces between the customer and supplier.
- Exchange of all necessary information and documentation between customer and supplier.
- Monitoring of supplier activities against agreed-upon requirements.
- Review of technical development with the supplier at predefined milestones.
- Tracking of progress against agreed-upon commitments.
- Implementation of corrective actions when progress deviates significantly from expectations.
2. The Supplier Monitoring Process
2.1 Establishing Joint Processes and Interfaces
Effective supplier monitoring begins with clear communication and alignment of processes. This involves:
- Defining roles and responsibilities for both customer and supplier teams.
- Establishing communication channels and protocols.
- Agreeing on project management methodologies and tools.
- Setting up shared documentation repositories and version control systems.
2.2 Information Exchange
Timely and accurate information exchange is crucial for effective monitoring. Key aspects include:
- Regular status reports from suppliers.
- Sharing of technical specifications and design documents.
- Prompt notification of any deviations or issues.
- Clear documentation of change requests and their impacts.
2.3 Technical Development Reviews
Periodic reviews of technical development ensure alignment with requirements and early detection of potential issues. These reviews typically involve:
- Design reviews at key development stages.
- Code reviews to ensure adherence to coding standards and best practices.
- Testing reviews to validate test coverage and results.
2.4 Progress Tracking
Continuous monitoring of supplier progress is essential for project success. This includes:
- Regular assessment of milestone achievements.
- Tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Monitoring of resource utilization and burndown rates.
- Evaluation of deliverable quality against predefined criteria.
2.5 Corrective Actions
When deviations from the plan are identified, prompt corrective actions are necessary:
- Root cause analysis of issues.
- Development and implementation of action plans.
- Follow-up to ensure effectiveness of corrective measures.
- Adjustment of project plans and timelines if necessary.
3. Best Practices for Effective Supplier Monitoring
3.1 Defining Clear Agreements
Clear and comprehensive agreements form the foundation of effective supplier monitoring:
- Detailed specification of deliverables and acceptance criteria.
- Clear definition of quality standards and performance metrics.
- Agreed-upon timelines and milestones.
- Specification of reporting requirements and frequencies.
3.2 Implementing Regular Communication Channels
Consistent and open communication is key to successful supplier monitoring:
- Scheduled status meetings with predefined agendas.
- Use of collaboration tools for real-time information sharing.
- Establishment of escalation procedures for critical issues.
- Regular face-to-face or virtual workshops for in-depth discussions.
3.3 Utilizing Performance Metrics
Quantitative metrics provide objective insights into supplier performance:
- On-time delivery rates.
- Defect density in delivered code.
- Test coverage percentages.
- Customer satisfaction scores.
3.4 Risk Management Strategies
Proactive risk management is crucial in supplier monitoring:
- Regular risk assessments and updates.
- Development of mitigation strategies for identified risks.
- Continuous monitoring of risk indicators.
- Incorporation of risk management into project planning and reviews.
4. Challenges in Supplier Monitoring
4.1 Cultural and Language Barriers
In global supply chains, cultural and language differences can pose significant challenges:
- Misinterpretation of requirements or feedback.
- Differences in work styles and communication norms.
- Varying perceptions of urgency and priority.
To address these challenges, organizations can:
- Provide cultural sensitivity training.
- Use clear, unambiguous language in all communications.
- Employ local liaisons or translators when necessary.
4.2 Alignment of Processes and Tools
Disparities in development processes and tools between customer and supplier can hinder effective monitoring:
- Incompatible project management methodologies.
- Different version control or bug tracking systems.
- Varying quality assurance processes.
Solutions include:
- Agreeing on a common set of tools and processes at project initiation.
- Providing training or support for adopted tools.
- Establishing clear interfaces between different systems when full alignment is not possible.
4.3 Managing Multiple Suppliers
When dealing with multiple suppliers, maintaining consistency and coordination becomes complex:
- Ensuring uniform quality standards across suppliers.
- Managing interdependencies between supplier deliverables.
- Balancing resources and attention across different supplier relationships.
Effective strategies include:
- Implementing a centralized supplier management system.
- Standardizing monitoring processes and metrics across suppliers.
- Conducting regular cross-supplier coordination meetings.
4.4 Ensuring Compliance Across the Supply Chain
Maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations throughout the supply chain is challenging:
- Varying levels of familiarity with automotive standards among suppliers.
- Ensuring traceability of compliance-related activities.
- Managing updates to standards and regulations.
To address this, organizations can:
- Provide training and resources on relevant standards to suppliers.
- Implement robust traceability tools and processes.
- Conduct regular compliance audits.
5. Data-Driven Supplier Monitoring
5.1 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Effective supplier monitoring relies on well-defined KPIs:
- Delivery Performance: Measures on-time delivery rate and adherence to schedules.
- Quality Metrics: Includes defect density, test coverage, and code quality scores.
- Communication Effectiveness: Assesses responsiveness and clarity of supplier communications.
- Innovation Index: Evaluates the supplier’s contribution to product innovation.
5.2 Automated Reporting Systems
Automation can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of supplier monitoring:
- Real-time dashboards for KPI tracking.
- Automated alerts for deviations from expected performance.
- Integration with project management and version control systems for comprehensive reporting.
5.3 Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment
Advanced analytics can provide early warning of potential issues:
- Trend analysis to identify patterns in supplier performance.
- Predictive models for estimating project outcomes based on current performance.
- Risk scoring algorithms to prioritize monitoring efforts.
6. The Future of Supplier Monitoring in Automotive SPICE
6.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are set to revolutionize supplier monitoring:
- Automated code review and quality assessment.
- Intelligent scheduling and resource allocation.
- Natural language processing for analyzing communication patterns and sentiment.
6.2 Blockchain for Transparent Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology offers potential for enhanced transparency and traceability:
- Immutable record of all supplier interactions and deliverables.
- Smart contracts for automated enforcement of agreements.
- Enhanced security and authenticity of shared information.
6.3 Evolving Industry Standards and Regulations
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, so too will the standards and regulations governing software development:
- Increased focus on cybersecurity in supplier monitoring processes.
- Integration of environmental sustainability metrics in supplier evaluation.
- Adaptation to emerging technologies like autonomous driving and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
7. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of ACQ.4
7.1 Case Study 1: Improving Supplier Performance
A major European automotive manufacturer implemented a comprehensive ASPICE ACQ.4 supplier monitoring process, resulting in:
- 30% reduction in software defects detected in late stages of development.
- 25% improvement in on-time delivery of supplier components.
- Significant increase in supplier satisfaction due to clearer communication and expectations.
7.2 Case Study 2: Reducing Project Delays and Costs
A global Tier 1 supplier adopted advanced data analytics in their supplier monitoring process:
- Predictive analytics helped identify potential delays 2-3 weeks earlier than traditional methods.
- Cost overruns were reduced by 15% through early intervention in at-risk projects.
- Resource allocation was optimized, leading to a 20% increase in overall project efficiency.
7.3 Case Study 3: Enhancing Quality Across the Supply Chain
A Japanese automaker implemented a blockchain-based supplier monitoring system:
- Achieved end-to-end traceability of software components across multiple tiers of suppliers.
- Reduced time spent on compliance audits by 40% due to immutable record-keeping.
- Improved collaboration and trust among suppliers, leading to faster innovation cycles.
Conclusion
Effective implementation of ASPICE ACQ.4 Supplier Monitoring is crucial for success in the increasingly software-driven automotive industry. By adopting best practices, leveraging data-driven approaches, and staying ahead of emerging trends, automotive companies can significantly enhance the quality, efficiency, and innovation in their software development processes.
Our company’s deep expertise in ASPICE consulting positions us uniquely to guide organizations through the complexities of supplier monitoring. We offer tailored solutions that not only ensure compliance with ASPICE standards but also drive tangible improvements in supplier performance, project outcomes, and overall product quality.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, robust supplier monitoring will remain a key differentiator for successful companies. By partnering with us, organizations can transform their supplier relationships from potential risks into powerful assets, driving innovation and excellence in automotive software development.