Executive Summary
In the rapidly evolving automotive software industry, measurement plays a crucial role in driving process improvement and organizational performance. ASPICE MAN.6 Measurement, a key process area within the Automotive SPICE framework, provides a structured approach to establishing and maintaining measurement capabilities. This whitepaper explores the intricacies of MAN.6, offering insights into its implementation, best practices, and future trends. By leveraging effective measurement strategies, automotive software companies can enhance decision-making, improve product quality, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
1. Introduction to ASPICE MAN.6 Measurement
1.1 Definition and Purpose
ASPICE MAN.6 Measurement is a process aimed at developing and sustaining a measurement capability used to support management information needs. It involves collecting, analyzing, and reporting data related to products developed and processes implemented within the organization. The primary purpose of MAN.6 is to provide objective information to support effective decision-making and performance improvement.
1.2 Importance in Automotive Software Development
In the context of automotive software development, MAN.6 is critical for several reasons:
- Quality Assurance: Measurement helps in monitoring and improving software quality throughout the development lifecycle.
- Process Optimization: It enables the identification of inefficiencies and bottlenecks in development processes.
- Risk Management: Quantitative data supports better risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
- Resource Allocation: Measurement insights allow for more effective allocation of time, budget, and personnel.
1.3 Relationship to Other ASPICE Processes
MAN.6 is closely interlinked with other ASPICE processes, providing valuable data and insights that support various aspects of automotive software development. For instance, it complements MAN.3 (Project Management) by offering quantitative project performance data, and supports SUP.1 (Quality Assurance) by providing metrics for quality assessment.
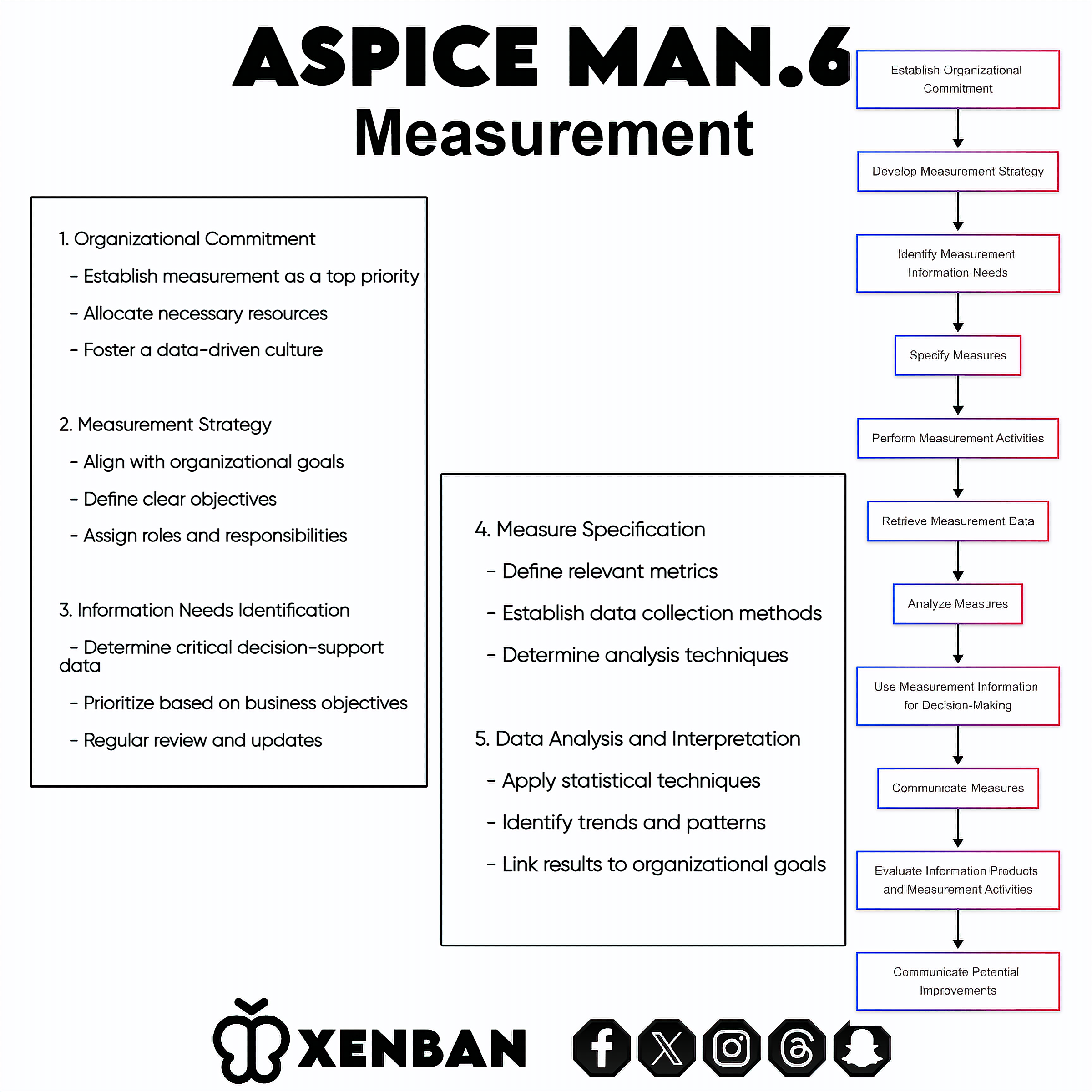
2. Key Components of MAN.6 Measurement
2.1 Organizational Commitment
Successful implementation of MAN.6 requires strong organizational commitment. This involves:
- Establishing measurement as a priority at all levels of the organization
- Allocating necessary resources for measurement activities
- Fostering a culture that values data-driven decision-making
2.2 Measurement Strategy
A well-defined measurement strategy aligns measurement activities with organizational goals. It should include:
- Clear objectives for the measurement program
- Scope of measurement activities
- Roles and responsibilities of stakeholders involved in measurement
2.3 Information Needs Identification
This component involves determining what information is required to support decision-making and process improvement. It includes:
- Identifying key stakeholders and their information needs
- Prioritizing information needs based on business objectives
- Documenting and reviewing information needs periodically
2.4 Measure Specification
Once information needs are identified, appropriate measures must be specified. This involves:
- Defining metrics that address identified information needs
- Establishing data collection methods and frequency
- Determining analysis techniques for collected data
2.5 Measurement Activities
This component encompasses the actual execution of measurement tasks, including:
- Data collection from various sources
- Data validation to ensure accuracy and reliability
- Data storage in a structured and accessible manner
2.6 Data Analysis and Interpretation
Collected data must be analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This includes:
- Applying statistical techniques to identify trends and patterns
- Interpreting results in the context of organizational goals
- Identifying areas for improvement based on analysis outcomes
2.7 Decision Support and Communication
The final component involves using measurement results to support decision-making and communicating findings to relevant stakeholders. This includes:
- Presenting measurement results in a clear and actionable format
- Using measurement insights to inform strategic and operational decisions
- Regularly communicating measurement outcomes to maintain stakeholder engagement
3. Implementing MAN.6 Measurement
3.1 Establishing Organizational Buy-in
To successfully implement MAN.6, it’s crucial to secure buy-in from all levels of the organization. This can be achieved by:
- Demonstrating the value of measurement through pilot projects
- Educating stakeholders on the benefits of data-driven decision-making
- Addressing concerns and resistance to measurement initiatives
3.2 Developing a Robust Measurement Strategy
A comprehensive measurement strategy should:
- Align with organizational goals and objectives
- Define clear metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Establish a timeline for implementation and review
3.3 Identifying and Prioritizing Information Needs
To effectively identify and prioritize information needs:
- Conduct workshops with key stakeholders to understand their requirements
- Use techniques like the Goal-Question-Metric (GQM) approach to derive metrics from business goals
- Regularly review and update information needs as organizational priorities evolve
3.4 Specifying Effective Measures
When specifying measures:
- Ensure measures are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound)
- Consider both process and product measures
- Balance leading and lagging indicators for a comprehensive view of performance
3.5 Performing Measurement Activities
Effective measurement activities involve:
- Automating data collection where possible to reduce manual effort and errors
- Implementing robust data validation processes
- Establishing a centralized measurement database for easy access and analysis
3.6 Analyzing and Interpreting Measurement Data
To derive meaningful insights from measurement data:
- Use statistical analysis techniques appropriate for the type of data collected
- Consider context when interpreting results (e.g., project size, complexity)
- Look for correlations between different measures to uncover deeper insights
3.7 Using Measurement Information for Decision-Making
To effectively use measurement information:
- Present data in visual formats (e.g., dashboards, charts) for easy comprehension
- Integrate measurement results into regular management reviews and decision-making processes
- Use measurement insights to drive continuous improvement initiatives
4. Best Practices for MAN.6 Measurement
4.1 Aligning Measures with Business Objectives
Ensure that all measures directly support organizational goals by:
- Regularly reviewing and updating measures to reflect changing business priorities
- Creating a clear linkage between measures and strategic objectives
- Involving senior management in the selection and review of key measures
4.2 Ensuring Data Quality and Reliability
Maintain high data quality by:
- Implementing rigorous data validation processes
- Providing training to staff involved in data collection and analysis
- Regularly auditing data collection and storage processes
4.3 Leveraging Automation in Data Collection and Analysis
Enhance efficiency and accuracy through automation:
- Implement tools for automated data collection from development and testing environments
- Use data analytics platforms for advanced analysis and visualization
- Explore machine learning techniques for pattern recognition and predictive analytics
4.4 Continuous Improvement of Measurement Processes
Foster a culture of continuous improvement by:
- Regularly reviewing and refining measurement processes
- Encouraging feedback from stakeholders on the usefulness of measurement information
- Benchmarking measurement practices against industry standards and best practices
5. Challenges and Solutions in MAN.6 Implementation
5.1 Common Pitfalls in Measurement Programs
Some common challenges include:
- Over-measuring, leading to data overload and analysis paralysis
- Focusing on easily measurable metrics rather than those that provide valuable insights
- Failing to act on measurement results, leading to disengagement
Solutions:
- Prioritize measures based on their impact on business objectives
- Regularly review and cull unnecessary metrics
- Establish clear action plans based on measurement insights
5.2 Overcoming Resistance to Measurement
Resistance often stems from fear of increased scrutiny or misuse of data. To address this:
- Clearly communicate the purpose of measurement as a tool for improvement, not punishment
- Involve team members in the design of measurement programs
- Demonstrate early wins to build trust and engagement
5.3 Balancing Cost and Value of Measurement
To ensure the measurement program delivers value:
- Regularly assess the cost-benefit ratio of measurement activities
- Focus on high-impact measures that directly support decision-making
- Leverage automation to reduce the overhead of measurement activities
6. Case Studies: Successful MAN.6 Measurement Implementation
6.1 Case Study 1: Improving Process Efficiency
A leading automotive software company implemented MAN.6 to improve its development process efficiency. By measuring cycle times and defect rates across different stages of development, they identified bottlenecks in their testing phase. This led to the implementation of automated testing tools, resulting in a 30% reduction in overall development time and a 25% decrease in post-release defects.
6.2 Case Study 2: Enhancing Product Quality
Another organization focused on using MAN.6 to enhance product quality. They implemented a comprehensive set of code quality metrics and integrated them into their continuous integration pipeline. This allowed for early detection of potential issues, leading to a 40% reduction in customer-reported bugs and a significant improvement in customer satisfaction scores.
6.3 Case Study 3: Driving Organizational Performance
A global automotive supplier used MAN.6 to drive overall organizational performance. By implementing a balanced scorecard approach that included measures across financial, customer, process, and learning perspectives, they were able to align their entire organization towards key strategic goals. This resulted in a 15% increase in market share and a 20% improvement in employee satisfaction over two years.
7. Future Trends in Automotive Software Measurement
7.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The future of MAN.6 measurement will likely see increased integration with AI and machine learning technologies. This could involve:
- Predictive analytics to forecast project outcomes based on historical data
- Automated anomaly detection in measurement data
- Natural language processing for analyzing qualitative feedback and requirements
7.2 Predictive Analytics in Measurement
Predictive analytics will play a larger role in measurement programs, enabling:
- Early warning systems for potential project risks or quality issues
- More accurate estimation of project timelines and resource needs
- Proactive identification of areas for process improvement
7.3 Evolving Standards and Best Practices
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, so too will measurement standards and best practices. Future trends may include:
- Greater emphasis on security and privacy metrics in light of connected car technologies
- Integration of measurement practices across the entire automotive supply chain
- Development of industry-wide benchmarks for key performance indicators
Conclusion
ASPICE MAN.6 Measurement is a critical process for automotive software organizations seeking to improve their performance and competitiveness. By providing objective data to support decision-making, drive process improvement, and enhance product quality, effective measurement programs can deliver significant value.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, with increasing complexity in software systems and growing emphasis on electric and autonomous vehicles, the importance of robust measurement practices will only increase. Organizations that can effectively implement and leverage MAN.6 will be well-positioned to navigate these challenges and opportunities.
Our company’s expertise in ASPICE consulting, combined with our deep understanding of MAN.6 implementation, positions us as an ideal partner for automotive software organizations looking to enhance their measurement capabilities. By leveraging our experience and best practices, companies can accelerate their journey towards data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement, ultimately leading to better products, more efficient processes, and improved business outcomes.